India’s selections on financial growth, development, and associated planetary boundary challenges have turn into all of the extra vital because it was declared essentially the most populous nation on the earth, overtaking China only a few months in the past. Moreover, India’s capital metropolis Delhi is en path to changing into the world’s most populous city agglomeration overtaking Tokyo by 2028. The nation’s 1.four billion residents, who’re more and more concentrated in cities, and have a younger median age of 28.2 (almost 10 years youthful than China’s median age of 39), want applicable financial growth planning that’s each equitable and sustainable.
The structure of Delhi-NCR
The engines of India’s development are the economies of its mega city-regions. Whereas nationwide and State-level insurance policies are very important to the nation’s financial growth, they aren’t sufficient to fulfill the wants of such city-regions. A working example is the Delhi Nationwide Capital Area (Delhi-NCR), whose prolonged city agglomeration straddles a number of State and metropolis jurisdictions, together with Faridabad, Ghaziabad, Gurugram, and Noida. The enlargement of the agglomeration has been vastly aided as a result of it being the nationwide capital in addition to numerous infrastructure investments such because the metro rail networks extending from the core to the periphery, and the proactive investments made by the contiguous States. Nevertheless, the peripheral contiguous cities are categorised individually within the financial and inhabitants Censuses. Being quickly urbanising suburbs, they lag behind the core of the Delhi Nationwide Capital Territory (Delhi-NCT) by way of infrastructure.
Map: Institutions and employment in agricultural and non-agricultural actions in Delhi NCR in 2013–14
Solely once we contemplate the info of this area spatio-economically can we recognise the entire agglomeration’s may, its labour pool, and its uneven growth.
Financial geography of Delhi-NCR
Delhi-NCR has the very best focus of jobs and folks within the nation, and generated a GDP of $370 billion in 2015. Its challenges embody rising land and infrastructure prices, rising revenue inequality, poor air high quality, land and water air pollution, the shortage of pure assets, and institutional coordination limitations. In our not too long ago launched report, the ‘Morphology of Delhi Nationwide Capital Area’s Financial Geography and its Implications for Planning’, a examine of sector-wise evolution of jobs in Delhi-NCR from liberalisation in 1991 as much as 2013–14 reveals that the core-periphery spatial system is in transition. The core has decentralised, as is clear from speedy horizontal constructed up space enlargement, infrastructure growth, and the peripheralisation of jobs and migrants. Nevertheless, this has not been accompanied by a shift to a high-wage, knowledge-based economic system within the core space. Casual work persists, unemployment charges have elevated, and girls’s participation within the workforce stays low. The area’s per capita revenue has tripled, and consumption ranges have risen, and the peripheries appeal to funding from their respective State governments. Gurugram and Gautam Buddha Nagar for instance are the districts with the very best per capita revenue in Haryana and U.P. respectively.
The density of jobs transferring outward from the centre of Delhi NCT
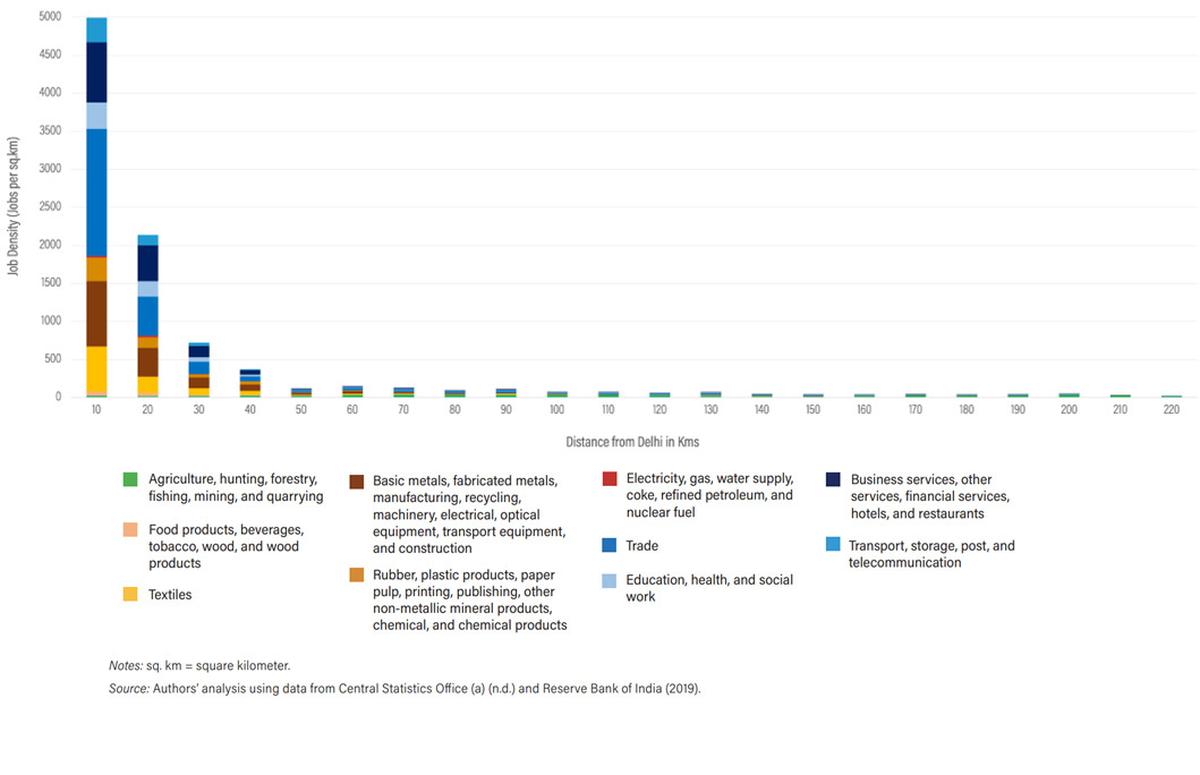
Delhi NCR presents a case of complementarity between its subregions, as a result of the roles that moved out from the ‘core’ had been captured by the periphery and the ‘remainder of the area’ with out getting expelled from the general area. The sectors that grew by way of industrial output generated extra employment than people who grew in technical and power effectivity. Conventional sectors corresponding to commerce, textiles and leather-based nonetheless dominate, however regardless of rising their employment share, their share to the area’s GDP has declined. On the entire, employment-intensive development within the secondary, tertiary sectors has been low. A spatial mapping of jobs by way of distance reveals that financial exercise peaked inside a 10 km radius of Delhi-NCT, and tapered off fully by 40 km.
The CAGR of employment throughout Delhi NCR’s three subregions from 1990 to 2013-14
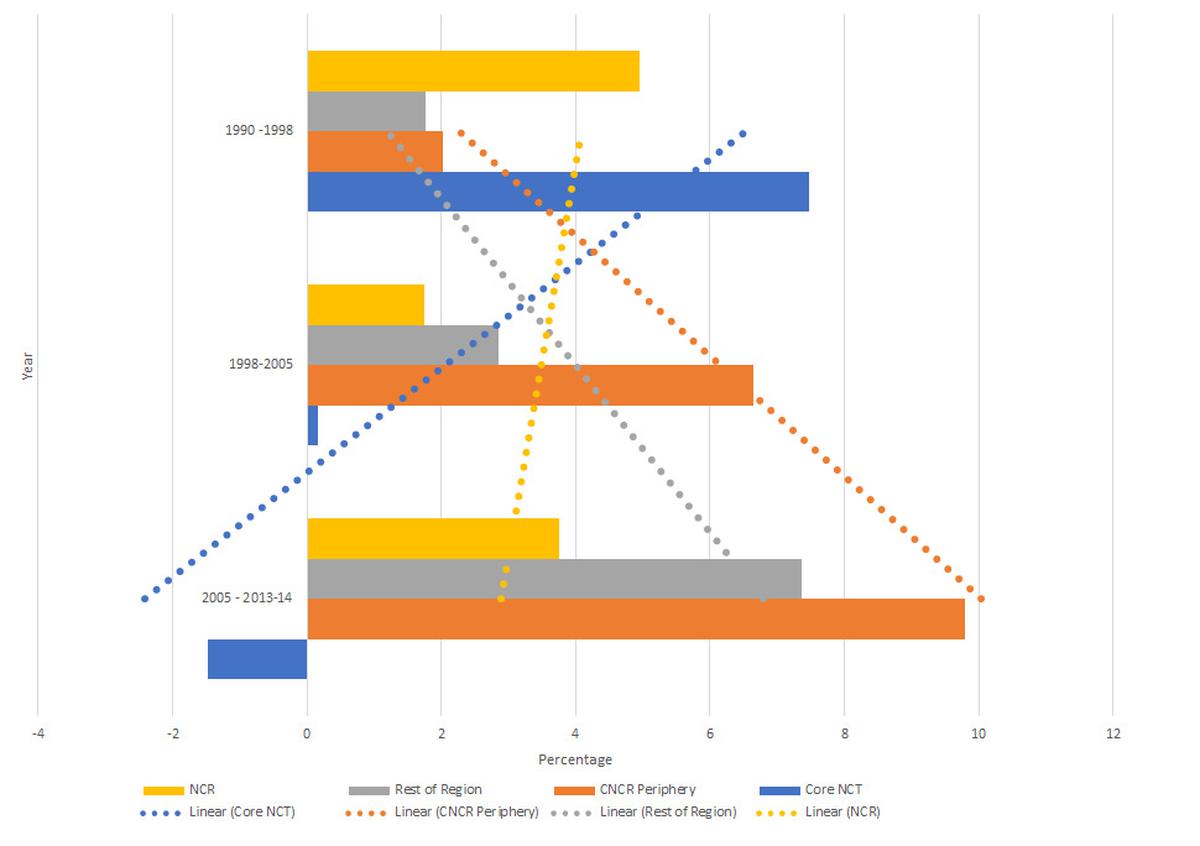
Decentralisation insurance policies, which had been emphasised way back to Delhi’s first grasp plan in 1962, coupled with land-use and constructing management restrictions, air pollution management norms, and inefficient land acquisition and disposal insurance policies, have contributed to the fragmented growth pushed by hypothesis past the boundaries of Delhi.
Classes for the International South
An financial geography strategy can successfully information the framing of more practical insurance policies, because it gives an interdisciplinary understanding of the place and why financial exercise happens, its related impression on individuals and that no two locations are alike.
Within the case of Delhi-NCR, for instance, a region-specific financial growth company may very well be created to leverage present interstate frameworks and create place-specific growth methods in a constantly up to date course of. This company might additionally foster wholesome competitors between collaborating cities and States to draw funding. On the similar time, a multi-stakeholder platform might be constructed to convey collectively the federal government, personal sector, industrial our bodies, academia, and civil society representatives, to deal with growth wants. An financial growth company can be arrange for the revitalisation of the Delhi-NCT core, as cities world wide have carried out to leverage their full potential.
In Delhi-NCR, as elsewhere, spatio-economic assessments will help goal infrastructure investments and overseas direct investments to economically dynamic areas, to make sure higher returns and job development. Methods, corresponding to secure and accessible work and journey, with baby and elder care amenities, might be deployed to allow ladies to take part within the economic system. Spatio-economic assessments may assist enhance entry to training, healthcare, fundamental providers, and jobs for marginalised teams.
An financial geography-based evaluation framework can facilitate higher planning and funding selections in mega city-regions, not simply in India but additionally elsewhere within the International South. It might inform planning processes on the regional and native ranges, information funding selections, think about environmental impacts, and facilitate the inclusion of marginalised teams within the economic system. Thus, it will probably assist guarantee well-planned, and inclusive financial development, and assist a better high quality of life whereas additionally valuing planetary assets.
Madhav Pai is CEO and Rejeet Mathews is Director, Built-in City Improvement at WRI India. Views are private.
